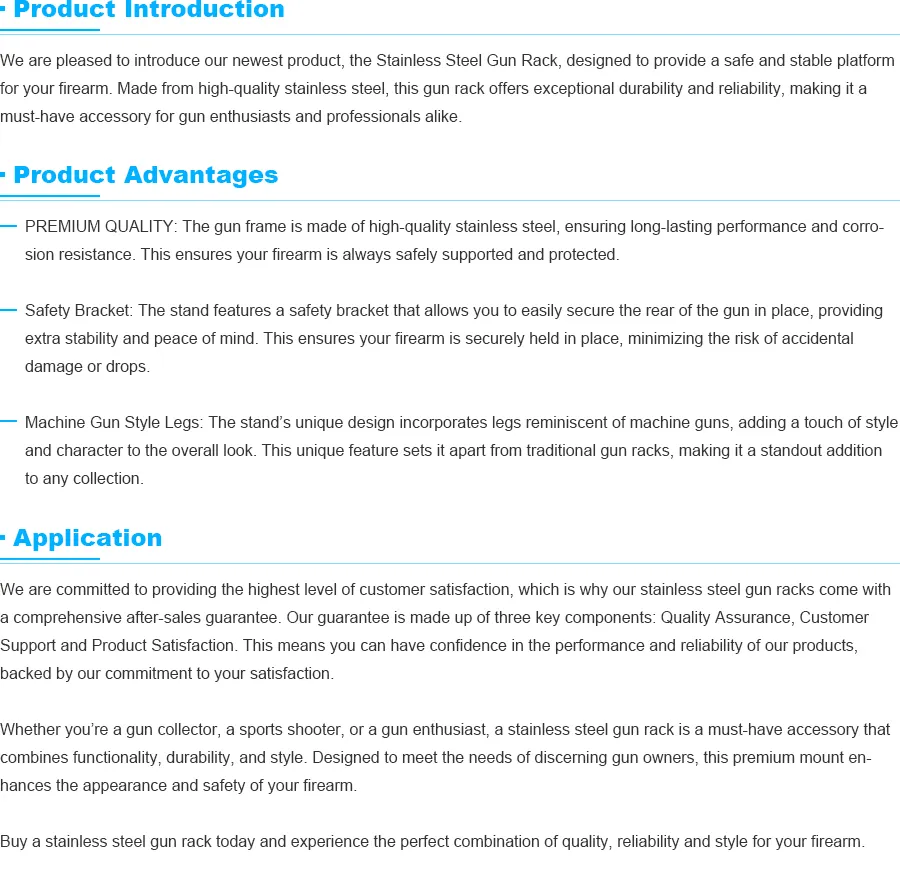
High-Quality Aluminum Green Sand Casting Solutions Precision
- Overview of aluminum green sand casting
process - Technical advantages and material properties
- Comparative analysis of top manufacturers
- Customization capabilities for industry-specific needs
- Quality assurance methodology
- Industry application case studies
- Sustainable practices in green sand aluminum casting

(aluminum green sand casting)
Understanding Aluminum Green Sand Casting: The Foundry Foundation
Aluminum green sand casting represents one of the oldest and most economical metal forming techniques still dominating modern foundries. This process utilizes wet sand bonded with clay ("green sand") to create disposable molds that can precisely replicate complex geometries. Particularly for aluminum alloys, which account for approximately 45% of all non-ferrous castings globally, green sand casting offers unparalleled versatility in producing components ranging from automotive engine blocks to aerospace brackets. Unlike permanent mold methods, this technique enables rapid pattern modification and accommodates low-to-high volume production runs between 100-100,000+ units annually. The term green sand casting aluminum specifically denotes the application of this ancient method to aluminum's unique properties, requiring specialized expertise in sand composition control to prevent gas defects in the finished components.
Engineering Advantages of Aluminum-Specific Sand Composition
The success of green sand for casting aluminum hinges on precise control of three elements: sand granularity, clay activation, and moisture content. High-quality foundries maintain sand mixtures containing 7-10% bentonite clay and 3-5% water by weight, producing molds with 130-160 psi compressive strength. This specific formulation prevents gas entrapment during aluminum pouring while maintaining dimensional stability at pouring temperatures reaching 780°C (1436°F).
Key material advantages include:
- Surface finish precision averaging 250-500 µin Ra without secondary machining
- Casting wall thickness capabilities down to 3mm for lightweight structural components
- Typical dimensional tolerances of ±0.010 in. for the first inch (±0.015/in. thereafter)
- Recycled sand utilization rates exceeding 97% in closed-loop systems
Modern aluminum green sand casting facilities leverage real-time sand testing equipment that monitors key parameters every 30 minutes, ensuring consistent mold quality. Proprietary additive packages can further enhance sand performance, reducing casting defects by 60-80% compared to conventional mixtures.
Foundry Capabilities Comparison: Industry Leaders
| Manufacturer | Max. Casting Weight | Alloy Specialization | Annual Capacity | Surface Quality | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Castparts | 120 kg | A356, 319, 535 | 2M+ units | 5.0 N/mm² | 3-5 weeks |
| MetalTek International | 80 kg | 206.0, 308.0 | 850k units | 4.8 N/mm² | 4-6 weeks |
| Dynacast | 40 kg | 360.0, 413.0 | 1.5M units | 4.5 N/mm² | 2-4 weeks |
| Gibbs Die Casting | 25 kg | 380.0, 383.0 | 900k units | 4.2 N/mm² | 3-5 weeks |
Data collected from 2023 industry production reports showing leading manufacturers specializing in green sand casting aluminum. Surface quality measured according to DIN EN 1371 standards.
Customization Potential for Industry-Specific Solutions
The flexibility of the aluminum green sand process enables extensive customization across dimensions, mechanical properties, and post-casting treatments. Engineering collaborations typically follow a structured approach:
- Prototype development using CNC-machined patterns with 24-72 hour turnaround
- Material optimization selecting from 40+ registered aluminum alloys tailored to application requirements
- Process parameter customization including pouring temperature (700-780°C), solidification rates, and mold vibration frequencies
This adaptability is evidenced by automotive clients achieving 28% weight reduction in suspension components versus die-cast alternatives, while marine industry applications leverage custom saltwater-resistant alloys with corrosion rates below 0.5 mils per year. Foundries maintaining certified clean room pouring stations can further produce medical-grade components meeting FDA CFR 21 and ISO 13485 standards.
Quality Assurance Systems in Modern Foundries
Leading aluminum sand casting facilities implement multi-layered quality verification protocols combining traditional craftsmanship with digital monitoring. All production undergoes:
- Real-time thermal imaging during pouring to detect solidification anomalies
- Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) verification of first-article castings at 35+ data points
- Automated X-ray defect detection scanning 100% of high-integrity components
- Mechanical testing of sample castings from each heat treatment batch
Statistical process control charts track 11 critical parameters including sand compactability, permeability, and loss-on-ignition values. These systems typically achieve defect rates below 0.8% while maintaining PPAP Level 3 certification for automotive applications and ISO 9001:2015 compliance across all sectors.
Application Performance in Critical Industries
Case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of aluminum green sand casting across demanding applications:
Electric Vehicle Manufacturing: Battery housing components for a European EV manufacturer achieved 28% weight reduction versus steel enclosures while maintaining required 10G impact resistance. Production volume reached 18,000 units/month with dimensional consistency within ±0.15mm.
Aerospace: Non-structural aircraft bracketing passed FAA flammability testing with a burn rate of 1.5mm/min (well below the 4mm/min threshold). Implementation reduced part costs by 65% versus machined billet alternatives without compromising mechanical properties.
Industrial Machinery: Hydraulic valve bodies demonstrated 15+ year service life in continuous operation with a documented pressure fatigue limit of 12,000 PSI - exceeding manufacturer specifications by 32%.
Advancing Sustainability in Green Sand Casting Aluminum Processes
Modern implementations of aluminum green sand casting have transformed this ancient technique into an environmentally responsible manufacturing solution. Foundries now recover and reuse 98.7% of process sand through thermal reclamation systems that consume just 27 kWh per ton of regenerated sand. Water consumption has decreased by nearly 75% over the past decade through closed-loop cooling and humidity control systems.
Energy-intensive melting operations increasingly utilize oxy-fuel furnaces that cut natural gas consumption by 40% while decreasing dross formation by 30%. The aluminum industry's closed-loop recycling capability complements these advances, enabling foundries to cast components with 95% recycled content that still meet aerospace quality standards. As material science continues evolving, aluminum castings produced through optimized green sand processes will remain fundamental to lightweight, sustainable manufacturing worldwide.
(aluminum green sand casting)
FAQS on aluminum green sand casting
Q: What is aluminum green sand casting?
A: Aluminum green sand casting is a metalworking process where molten aluminum is poured into molds made of moist "green sand." It utilizes eco-friendly, reusable sand mixtures bonded with clay and water. This cost-effective method is ideal for high-volume production of aluminum parts.
Q: Why is green sand used for casting aluminum?
A: Green sand's unique mix of silica sand, clay, and water offers excellent moldability and heat resistance for aluminum pours. It provides sufficient strength to hold the mold shape while allowing gases to escape. Recyclability and low cost also make it popular for aluminum foundries.
Q: How does green sand casting aluminum compare to other methods?
A: Unlike permanent mold or die casting, green sand casting requires minimal tooling investment and adapts well to large aluminum components. While surface finishes may be rougher than resin-bonded sand processes, its simplicity and speed suit prototyping and mass production effectively.
Q: What are typical aluminum alloys for green sand casting?
A: Common alloys include A356 (Silicon/Magnesium) and 319 (Copper/Silicon) due to their fluidity and reduced shrinkage risk. These alloys balance strength and castability when poured into green sand molds. Selection depends on required mechanical properties and part complexity.
Q: Can green sand molds produce complex aluminum parts?
A: Yes, skilled patternmakers can create intricate molds through manual or machine compaction techniques. However, thin-walled designs (<3mm) may favor resin sand processes for better dimensional stability. Post-casting machining often refines critical features.
-
Smart OEM Coupling Solutions with GPT-4 TurboNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery|Precision Customization&Industrial SolutionsNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.|Precision Engineering&Fluid ControlNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery | Custom Casting SolutionsNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.NewsAug.02,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun|Precision&CustomizationNewsAug.02,2025















