Fév . 19, 2025 03:38
Back to list
stamping parts for sale
Understanding the intricate world of stamping dies demands a deep dive into both the macro and micro-components that collectively ensure precision in metal fabrication. A stamping die, integral to the manufacturing industry, is a specialized tool used to cut or shape metal using a press. Each part plays a crucial role in this process, offering remarkable precision and efficiency in producing complex components. This exploration of the parts of a stamping die reveals not only the surprising sophistication behind these tools but also why they are indispensable in advanced manufacturing.
Equally significant in the assembly of a stamping die is the consideration for dies’ maintenance and lifespan. As these components are subjected to high pressures, they must be regularly inspected, maintained, and replaced as needed to reduce downtime and maintain production quality. The construction of a stamping die also involves the development of specialized coatings for components like punches and die blocks. These coatings reduce friction and enhance the hardness of the tool surfaces, significantly extending their operational life and improving performance. Advanced technologies in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) have revolutionized the development of stamping dies, increasing the complexity of designs that can be fabricated with precision. Engineers can now simulate various stamping operations digitally, enabling the optimization of die components before physical production begins. This technological synergy allows for the creation of highly intricate metal parts with reduced trial and error, saving both time and resources. Incorporating feedback loops from real-world usage back into the design and manufacturing processes of stamping dies emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement and innovation. Industry experts continually gather data on wear patterns, operational efficiency, and failure points to develop enhanced designs that offer greater reliability and efficiency. Trust in stamping dies is bolstered by rigorous quality control processes. Every die is subjected to stringent testing and inspection to ensure that it meets the exacting standards of industrial manufacturing. This adherence to quality ensures the delivery of components that are not only precise but also consistent, enhancing their reputation as reliable tools in metal fabrication. Overall, understanding the individual roles of each part of a stamping die reveals a finely tuned system, where precision, craftsmanship, and technology converge to produce high-quality, consistent metal products. With continued technological advancements, the functionality and capabilities of stamping dies will further expand, continuing to meet the evolving demands of the manufacturing landscape with authority and trustworthiness.

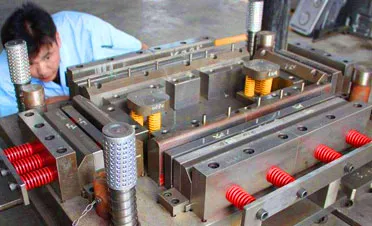
Equally significant in the assembly of a stamping die is the consideration for dies’ maintenance and lifespan. As these components are subjected to high pressures, they must be regularly inspected, maintained, and replaced as needed to reduce downtime and maintain production quality. The construction of a stamping die also involves the development of specialized coatings for components like punches and die blocks. These coatings reduce friction and enhance the hardness of the tool surfaces, significantly extending their operational life and improving performance. Advanced technologies in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) have revolutionized the development of stamping dies, increasing the complexity of designs that can be fabricated with precision. Engineers can now simulate various stamping operations digitally, enabling the optimization of die components before physical production begins. This technological synergy allows for the creation of highly intricate metal parts with reduced trial and error, saving both time and resources. Incorporating feedback loops from real-world usage back into the design and manufacturing processes of stamping dies emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement and innovation. Industry experts continually gather data on wear patterns, operational efficiency, and failure points to develop enhanced designs that offer greater reliability and efficiency. Trust in stamping dies is bolstered by rigorous quality control processes. Every die is subjected to stringent testing and inspection to ensure that it meets the exacting standards of industrial manufacturing. This adherence to quality ensures the delivery of components that are not only precise but also consistent, enhancing their reputation as reliable tools in metal fabrication. Overall, understanding the individual roles of each part of a stamping die reveals a finely tuned system, where precision, craftsmanship, and technology converge to produce high-quality, consistent metal products. With continued technological advancements, the functionality and capabilities of stamping dies will further expand, continuing to meet the evolving demands of the manufacturing landscape with authority and trustworthiness.
Next:
Latest news
-
Precision Lost Wax Casting Factories | AI-Powered QualityNewsAug.04,2025
-
Smart OEM Coupling Solutions with GPT-4 TurboNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery|Precision Customization&Industrial SolutionsNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.|Precision Engineering&Fluid ControlNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery | Custom Casting SolutionsNewsAug.03,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.NewsAug.02,2025
PRODUCTS CATEGORIES















