Precision Stamped Steel Parts - Durable & Custom Solutions
- Overview of Stamped Steel Parts Manufacturing
- Technical Advantages in Precision Stamping
- Performance Comparison: Top 5 Global Suppliers
- Customization Strategies for Industrial Applications
- Case Study: Automotive Component Production
- Quality Assurance & Compliance Standards
- Future Trends in Steel Stamped Parts Innovation

(stamped steel parts)
Understanding Stamped Steel Parts Manufacturing
Stamped steel parts form the backbone of modern industrial manufacturing, with the global market valued at $265.8 billion in 2023 (GMI Research). These components undergo precision forming processes where:
- High-speed presses apply 15-2,500 tons of force
- Material thickness ranges from 0.13mm to 6.35mm
- Tolerances achieve ±0.025mm for critical applications
Technical Superiority in Metal Stamping
Advanced stamped steel parts
manufacturers employ servo-electric presses reducing energy consumption by 40-60% compared to mechanical systems. Key technological differentiators include:
| Feature | Standard Stamping | Premium Stamping |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | 120-180 SPM | 300-400 SPM |
| Tool Life | 500k cycles | 2M+ cycles |
| Scrap Rate | 4.2-5.8% | 0.8-1.2% |
Global Supplier Benchmark Analysis
The stamped components sector shows significant performance variations across manufacturers:
| Manufacturer | Annual Capacity | Tolerance (±mm) | Material Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | 85M units | 0.05 | 12 grades |
| Supplier B | 120M units | 0.10 | 8 grades |
| Supplier C | 45M units | 0.025 | 18 grades |
Tailored Production Solutions
Leading providers now offer modular production systems enabling:
- Rapid prototyping within 72 hours
- Dual-source tooling agreements
- Multi-material stacking capabilities
Customization parameters typically include:
- Material thickness (0.2-8mm)
- Surface treatments (Zn-Ni, Dacro, E-coat)
- Post-stamping operations (welding, assembly)
Automotive Application Case Study
A Tier 1 supplier reduced chassis component weight by 22% through advanced stamped steel parts integration:
- Cycle time reduction: 18% (from 8.2s to 6.7s)
- Material utilization: Improved to 93.4%
- Annual production: 2.7M units
Quality Management Systems
ISO 9001:2015-certified facilities maintain:
- 100% first-article inspection
- Statistical process control (Cpk ≥1.67)
- Digital traceability systems
Innovating Stamped Steel Parts Technology
The industry anticipates 7.9% CAGR through 2030, driven by:
- AI-powered predictive maintenance systems
- Ultra-high-strength steel alloys (1,500 MPa+)
- Hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing
Stainless steel stamped parts now account for 34% of the medical equipment sector, demonstrating the material's expanding application range.
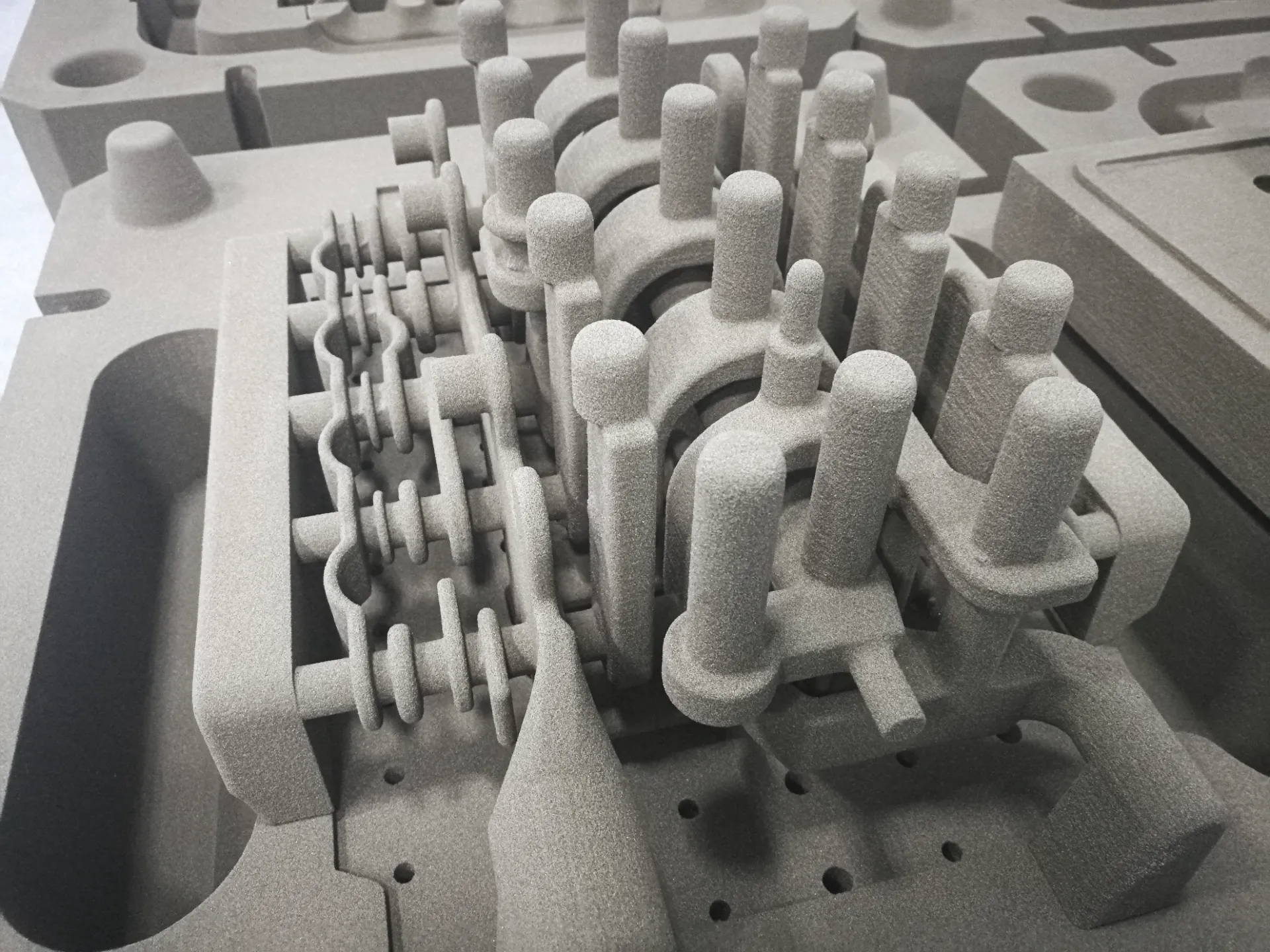
(stamped steel parts)
FAQS on stamped steel parts
Q: What are the primary applications of stamped steel parts?
A: Stamped steel parts are widely used in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and appliances. They provide cost-effective solutions for components like brackets, connectors, and housings. Their durability and precision make them ideal for high-volume production.
Q: How do stainless steel stamped parts resist corrosion?
A: Stainless steel stamped parts contain chromium, which forms a passive oxide layer to prevent rust. This makes them suitable for harsh environments like medical equipment or food processing. They maintain structural integrity while resisting chemical exposure.
Q: What materials are commonly used for steel stamped parts?
A: Common materials include cold-rolled steel, galvanized steel, and stainless steel. Selection depends on factors like strength requirements, corrosion resistance, and budget. Specialty alloys may be used for extreme temperature or wear resistance.
Q: What advantages do stamped steel parts offer over machined components?
A: Stamped steel parts enable faster production and lower per-unit costs for large batches. The process minimizes material waste compared to machining. Complex shapes can be achieved with tight tolerances using progressive die stamping.
Q: How to ensure quality in stainless steel stamped parts manufacturing?
A: Quality is ensured through precision tooling design and CNC-controlled stamping presses. Regular material testing and dimensional inspections validate consistency. Secondary processes like deburring or plating further enhance performance and finish.
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery|Precision Engineering,Customizable Sand CastingNewsAug.11,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery|Precision Engineering, CustomizableNewsAug.11,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.NewsAug.11,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery And Equipment Trading Co., Ltd.NewsAug.11,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings-Baoding Hairun Machinery|Precision Casting,CustomizationNewsAug.10,2025
-
OEM Sand Cast Pump Valve Fittings - Baoding Hairun Machinery | Custom Casting, Quality AssuranceNewsAug.10,2025















